armor.wikisort.org - Tank
The Centauro is a family of Italian military vehicles originating from a wheeled tank destroyer for light to medium territorial defense and tactical reconnaissance. It was developed by a consortium of manufacturers, the Società Consortile Iveco Fiat - OTO Melara (CIO). Iveco Fiat was tasked with developing the hull and propulsion systems while Oto Melara was responsible for developing the turrets and weapon systems.[2]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2013) |
| Centauro | |
|---|---|
 An Italian Army Centauro during a patrol in Bosnia-Herzegovina as part of IFOR during 1996 | |
| Type | Wheeled tank destroyer |
| Place of origin | Italy |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1991–present |
| Used by | See Operators below |
| Wars | Iraq War UNIFIL (United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon) |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1986 |
| Manufacturer | Iveco Fiat (hull, propulsion) Oto Melara (weapons, turrets) |
| Unit cost | €1.6 million [citation needed] |
| Produced | 1991–2006 |
| No. built | 490+ (plus 249 Freccia[1][unreliable source?]) |
| Variants | See Variants |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 24,000 kg (26 short tons) |
| Length | 7.85 m (25 ft 9 in) |
| Width | 2.94 m (9 ft 8 in) |
| Height | 2.73 m (8 ft 11 in) |
| Crew | 4 (commander, gunner, loader and driver) |
| Armor | Welded steel armoured hull |
Main armament | Oto Melara 105 mm/52 rifled gun (Centauro) Oto Melara 120mm /45 smoothbore gun (Centauro II) |
Secondary armament | 2×7.62 mm MGs |
| Engine | IVECO, V6 turbo-Diesel 520 hp (382 kW) |
| Power/weight | 19.35 hp/tonne |
| Transmission | Hydropneumatic automatic transmission with 5 forward and 2 reverse gears 8x8 wheels |
| Suspension | independent MacPherson struts |
Operational range | 800 km (500 mi) |
| Maximum speed | 108 km/h (67 mph) |
Over the years, the Centauro platform has been developed into multiple variants to fulfill other combat roles, such as infantry fighting vehicle or self-propelled howitzer.
Description
The vehicle was developed in response to an Italian Army requirement for a tank destroyer with the firepower of the old Leopard 1 main battle tank then in service with the Italian Army, but with greater strategic mobility. The main mission of the Centauro is to protect other, lighter, elements of the cavalry, using its good power-to-weight ratio, excellent range and cross country ability (despite the wheeled design) and computerized fire control system to accomplish this mission. Centauro entered production in 1991 and deliveries were complete by 2006.[3]
Armament

The main armament consists of the Oto Melara 105 mm/52 caliber gyro-stabilized high-pressure, low-recoil gun equipped with a thermal sleeve and an integrated fume extractor, with 40 rounds: 14 ready rounds in the turret and another 26 rounds in the hull. The gun can fire standard NATO ammunition, including APFSDS (Armour Piercing Fin-Stabilized Discarding Sabot) rounds.
Secondary weapons are a 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun, and another 7.62 mm anti-aircraft machine gun with 4,000 rounds of ammunition.
Aiming is provided by a Galileo Avionica TURMS fire control system (the same as fitted to the Italian Ariete tank) and is equipped with a muzzle referencing system and a fully digital ballistic computer. The gunner's sight is fully stabilized and comes equipped with a thermal imager and laser rangefinder. The commander's station is equipped with a panoramic stabilized sight, an image intensifying night sight and a monitor displaying the image from the gunner's thermal sight. This allows Centauro to engage stationary or moving targets while stationary or on the move, in day or night.[4]
Armour
The Centauro hull is an all-welded steel armoured hull, which in the baseline configuration is designed to withstand 14.5 mm bullets and shell fragments with protection against 25 mm munition on the frontal section. The addition of bolt-on appliqué armour increases protection against 30 mm rounds.
The Centauro is also equipped with an CBRN (Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear) warfare protection system, which is integrated with the vehicle's air conditioning system. The vehicle is also equipped with a four-barreled smoke grenade launcher mounted on each side of the turret and a laser warning receiver.[4]
Propulsion
Centauro is powered by an Iveco V6 turbo-charged after-cooled diesel engine delivering 520 hp (382.4 kW). This drives a ZF-designed automatic transmission, which is manufactured under license by Iveco Fiat. The transmission system has five forward and two reverse gears. This drives eight wheels, which are each equipped with an independent suspension system, and, furthermore, equipped with run-flat inserts and a Central Tyre Inflation System (CTIS). Braking is provided by eight disc brakes. Steering is provided on the first and second axles and at slow speed also with the fourth axle. Together, this allows Centauro to achieve road speeds in excess of 100 km/h, negotiate gradients up to 60%, ford water up to a depth of 1.5m without preparation, and have a turning radius of 9m.[4]
Combat history
It is currently deployed as part of UNIFIL forces in Lebanon.[5]
Centauro was deployed in the former Yugoslavia and Somalia, where the design proved successful. Centauro was usually employed to escort motor convoys, for wide area control and for road patrols.[6]
Centauros were also deployed during operation Antica Babilonia, the Italian involvement in the Iraq War. During this operation, a Centauro troop took part in the battle for the bridges of Nassiriya, destroying a building where snipers were hiding.
In 2003, Spain deployed six Centauro 105/52mm to Iraq for the self-defense of their troops.[7]
Variants
Anti-tank

- Centauro 105mm
- The baseline and original version, also called Centauro Reconnaissance Anti-Tank.


- Centauro 120mm
- Upgraded Centauro with a low recoil 120 mm L/45 cannon (unrelated to the Rheinmetall L/44 120mm) in a newly designed turret and with new composite armour that can resist up to 40mm APFSDS rounds on the front and 14.5mm on the rest of the body.[8] This vehicle was also used as a testbed for various technologies that would be used in the B1 Centauro's successor vehicle, the Centauro II.[9]
Other roles
- VBM "Freccia"
- The Veicolo Blindato Medio "Freccia" (Italian: Medium Armoured Vehicle "Arrow") is a reconfigured[10] Centauro to act as a wheeled infantry fighting vehicle with multiple variants, such as command & control or mortar carrier, offering increased armour and NBC protection. It can transport up to eight infantrymen plus three crew.
- Centauro 155/39LW
- Added to the Centauro range in late 2013 to fill the role of self-propelled howitzer,[11] being able to fire up to 8 rounds/minute to a distance exceeding 60km for guided ammunition. It mounts an ultralight 155mm/39 main gun, based on the latest material breakthroughs,[12] and a secondary 7.62 or 12.7mm MG. The 155/39 is manned by a crew of two and provides full NBC and ballistic protection.[13]
- Centauro VBM Recovery
- Serves both as an engineer vehicle and for recovery and repair of damaged armoured vehicles on the battlefield.[14]
- Draco
- The Draco was never completed, and remained as an unfinished prototype. The only functional part of the Draco was the hull itself which was just a B1 Centauro, the actual weapon system remained a mock up and would not be completed. The Draco was supposed to be armed with revolver-type ammunition loading system. It can use all standard 76 mm ammunition, guided DART ammunition, C-RAM and top-attack ammunition and fully compatible with all in service 76mm rounds. Rate of fire is 80-100 rounds per minute (depending on the elevation angle). Ammunition revolver contains 12 indexed rounds and can shift from one type of ammunition to another.
Operators
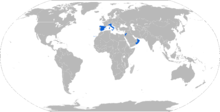
Current operators
 Italy: 259 B1 Centauro.[15] Total production was 400, with the remaining 141, all from the older versions, exported to Jordan.[16]
Italy: 259 B1 Centauro.[15] Total production was 400, with the remaining 141, all from the older versions, exported to Jordan.[16] Jordan: 141 B1 Centauro (all ex-Italian Army); some donated as Italian military aid and modernized with upgrade kits.[17]
Jordan: 141 B1 Centauro (all ex-Italian Army); some donated as Italian military aid and modernized with upgrade kits.[17] Oman: 9 B1 Centauro; modified variant with 120mm gun.[17]
Oman: 9 B1 Centauro; modified variant with 120mm gun.[17] Spain: 84 B1 Centauro, designated VRCC in Spanish service; 4 VCREC recovery vehicles.[17]
Spain: 84 B1 Centauro, designated VRCC in Spanish service; 4 VCREC recovery vehicles.[17]
Evaluation-only operators
 Russia: A 120mm gun-armed version was tested by the Russian army, alongside the standard 105mm-armed version. They were returned to Italy after tests were complete.[18]
Russia: A 120mm gun-armed version was tested by the Russian army, alongside the standard 105mm-armed version. They were returned to Italy after tests were complete.[18] United States: Leased 16 Centauro between 2000 and 2002 for evaluation, and to gain experience for the introduction of the Stryker Mobile Gun System.[19]
United States: Leased 16 Centauro between 2000 and 2002 for evaluation, and to gain experience for the introduction of the Stryker Mobile Gun System.[19]
References
- "VBM Freccia Infantry Fighting Vehicle, Italy". Army-Technology.com. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- "CENTAURO I". www.iveco-otomelara.com. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- "B1 Centauro". Tank Encyclopedia. 1 December 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- "Centauro B1 Tank Destroyer | Military-Today.com". www.military-today.com. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- "CIO Centauro 8x8 Tank Destroyer". Military Factory. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- "B1 Centauro tank destroyer / VBC 8x8 APC".
- "España refuerza su despliegue en Iraq con seis blindados con cañones de gran calibre". Belt Iberica (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 10 February 2015. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- "Centauro II MGS 120/105".
- Centauro with 120 mm Gun, Military-Today, accessed 23/02/2021
- "Centauro VBM". Deagel.com. Retrieved 15 June 2016.
- "Self-Propelled Wheeled Howitzer Centauro 155/39LW" (PDF). otomelara.it. Oto Melara. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 August 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- "Artillery on wheels". armada.ch. Armada International. Archived from the original on 11 August 2018. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- "Centauro 155 39LW". otomelara.it. Oto Melara. Archived from the original on 21 August 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- "Centauro VBM Recovery". Deagel.com. Retrieved 15 June 2016.
- The International Institute< for Strategic Studies - The Military Balance 2017, pag.128
- "La grande svendita delle armi (usate) italiane (The great sale of the Italian army)". Il Sole 24 Ore (in Italian). Archived from the original on 28 August 2014. Retrieved 28 August 2014.
- "Trade Registers". Armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "Russia Testing Italian Tank". en.rian.ru. RIA Novosti. 12 May 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
- "Centauro B1". Military Today.com. Retrieved 21 January 2011.
External links
На других языках
[de] Centauro
Der Centauro (dt. Kentaur) ist ein italienischer 8×8-Radpanzer, der in der ersten Version in den 1990er Jahren in Dienst gestellt wurde. Das Nachfolgemodell Centauro 2 (oder Centauro II) wird seit 2019 produziert. Aus diesen beiden Modellen wurden verschiedene Spezialfahrzeuge entwickelt.- [en] B1 Centauro
[ru] Centauro
«Чентауро» (итал. Centauro) — итальянская боевая машина с тяжёлым вооружением, часто классифицируемый также как истребитель танков.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии